Cross Border Electricity Trade in South Asia and India’s Pivotal Role
-
Energy Sector July 29, 2025By Arunima Mishra

CBET (Cross Border Electricity Trade) enables regional cooperation, optimizing resource sharing and grid stability to meet growing electricity needs sustainably. The South Asia (SA) region is blessed with diverse natural resources and enormous potential for renewable energy (RE) resources. With abundant renewable energy resources, South Asia can leverage cross-border power trade to accelerate its clean energy transition. Enhancing regional electricity trade in South Asia offers a viable pathway to secure stable and sufficient power supply. This potential stems from complementary demand-supply dynamics across nations, driven by varying energy resource endowments and seasonal consumption patterns.
The renewable energy resources spread across South Asian nations remain underdeveloped due to varied reasons and gaps. India’s leadership in regional energy integration stems from its unique combination of technical capabilities, economic influence, and geographic centrality.
Among the eight South Asian nations, CBET is presently confined to the BBIN countries (Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal). The trade mechanism combines bilateral PPAs under intergovernmental MOUs and market-based transactions through India’s IEX platform
Cross Border Electricity Trade between India and Neighbouring countries
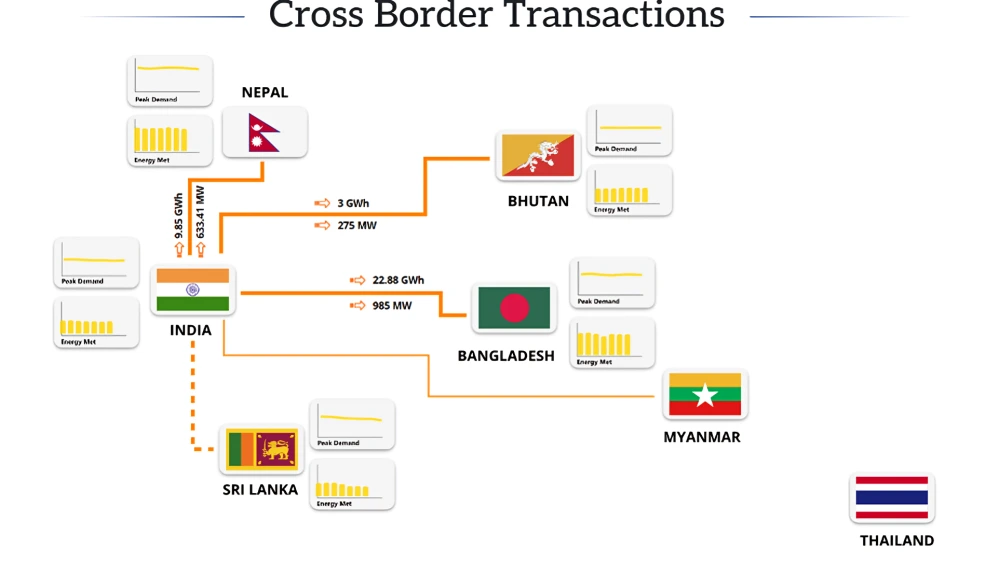
India-Bangladesh: Since 2013, Bangladesh has imported electricity from India, strengthening bilateral energy ties.
India-Bhutan: Bhutan serves as a crucial hydropower supplier to India, with approximately 70-80% of its generated electricity exported at preferential tariffs.
Most projects are developed through joint ventures between power utilities from India and Bhutan’s Druk Green Power Corporation (DGPC).
India-Nepal: Electricity trade has expanded significantly in recent years, transitioning from Nepal’s one-way imports to exchange in bilateral mode. Nepal now exports surplus hydropower to India, leveraging its growing generation capacity and India’s rising energy demand.
India-Myanmar: Limited cross-border trade exists, primarily supplying power to border areas, with potential for future hydropower exports under discussion.
India on the Forefront
India has emerged as a driving force in regional energy cooperation through its pioneering role in multilateral electricity trade. The following initiatives proves India’s
- Strategic investments in cross-border transmission infrastructure, including the Bharampura-Bheramara line (India-Bangladesh) and multiple high-capacity interconnections with Nepal.
- A landmark tripartite agreement between India, Nepal, and Bangladesh, facilitating the supply of 500 MW of Nepalese hydropower to Bangladesh via Indian transmission networks, enhancing regional energy synergy.
- Introduction of CBET guidelines (2018) and visionary proposals such as the “One Sun, One World, One Grid” (OSOWOG) initiative, unveiled at the 2023 G20 Summit, to promote global renewable energy integration.
- Leadership in the International Solar Alliance (ISA), reinforcing its expertise in solar energy and sustainable power solutions.
- A pivotal role in BIMSTEC, leveraging platforms like the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway to strengthen economic and energy connectivity.
- Promotion of the electricity trade with different counties in the South Asia through Power Exchange, a proposed unified electricity marketplace to optimize cross-border power trading efficiency.
Energy cooperation in South Asia has progressed significantly, with cross-border electricity trade (CBET) moving beyond bilateral arrangements toward more structured regional frameworks. India has emerged as a central actor in this transformation, driving both energy cooperation and broader economic development across the region.